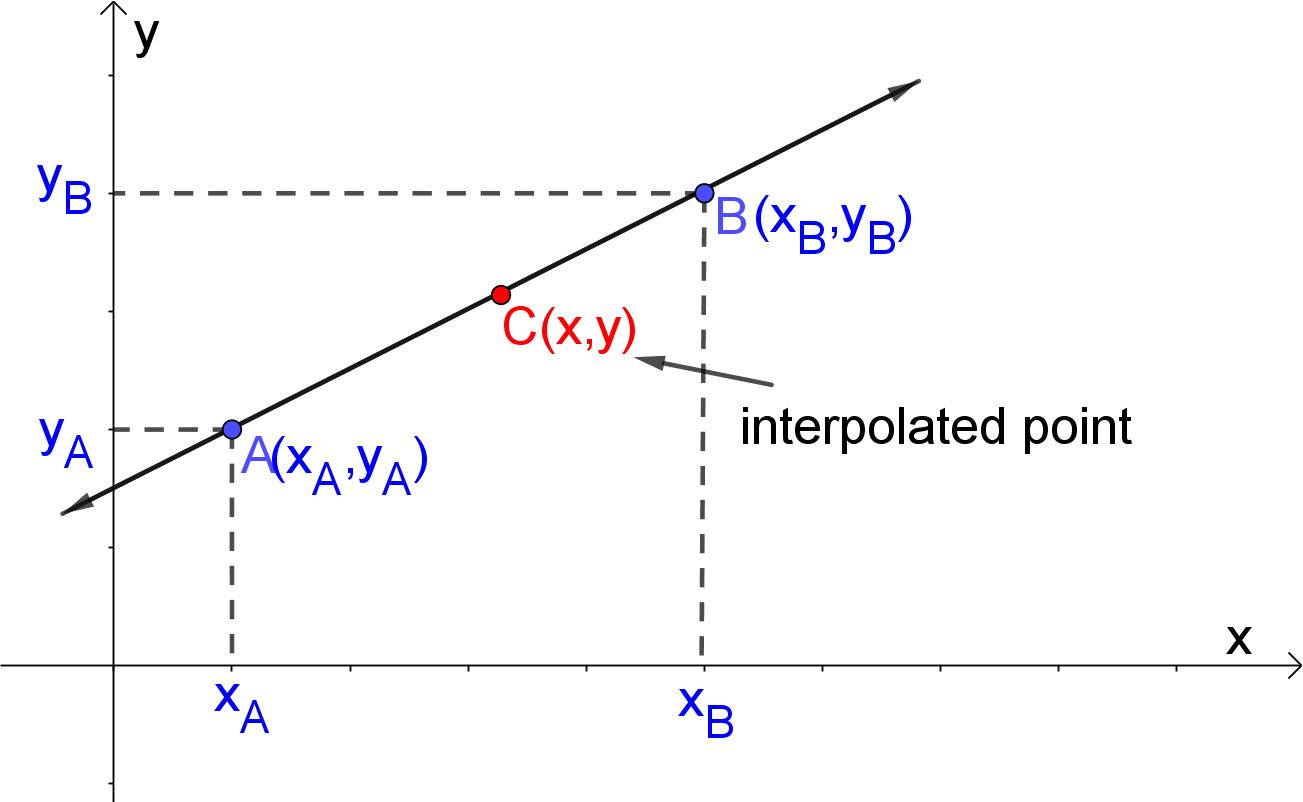
Linear Interpolation Derivation . Where a = unknown coefficients, i = 0 n. ( n + 1 coefficients). X = ao + a1x + a2x2 + a3x3 + + anxn. Linear interpolation is obtained by passing a straight line between 2 data points. we present linear, cubic hermite, and cubic spline interpolation methodologies, outlining the underlying assumptions and structural. interpolation is the problem of tting a smooth curve through a given set of points, generally as the graph of a function. since it is a linear interpolation, just consider a straight line $y=a+ bx$ which goes through two points $(x_0,y_0)$ and. G(x) f(x 1) f(x) f(x 0) x. it’s form is (expressed as a power series):
from ncalculators.com
interpolation is the problem of tting a smooth curve through a given set of points, generally as the graph of a function. Linear interpolation is obtained by passing a straight line between 2 data points. since it is a linear interpolation, just consider a straight line $y=a+ bx$ which goes through two points $(x_0,y_0)$ and. Where a = unknown coefficients, i = 0 n. we present linear, cubic hermite, and cubic spline interpolation methodologies, outlining the underlying assumptions and structural. ( n + 1 coefficients). G(x) f(x 1) f(x) f(x 0) x. it’s form is (expressed as a power series): X = ao + a1x + a2x2 + a3x3 + + anxn.
Linear Interpolation Calculator
Linear Interpolation Derivation ( n + 1 coefficients). ( n + 1 coefficients). interpolation is the problem of tting a smooth curve through a given set of points, generally as the graph of a function. X = ao + a1x + a2x2 + a3x3 + + anxn. it’s form is (expressed as a power series): G(x) f(x 1) f(x) f(x 0) x. since it is a linear interpolation, just consider a straight line $y=a+ bx$ which goes through two points $(x_0,y_0)$ and. we present linear, cubic hermite, and cubic spline interpolation methodologies, outlining the underlying assumptions and structural. Linear interpolation is obtained by passing a straight line between 2 data points. Where a = unknown coefficients, i = 0 n.
From calculators.io
Linear Interpolation Calculator & Formula [100 Free] Calculators.io Linear Interpolation Derivation we present linear, cubic hermite, and cubic spline interpolation methodologies, outlining the underlying assumptions and structural. Where a = unknown coefficients, i = 0 n. since it is a linear interpolation, just consider a straight line $y=a+ bx$ which goes through two points $(x_0,y_0)$ and. X = ao + a1x + a2x2 + a3x3 + + anxn. Linear. Linear Interpolation Derivation.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT POLYNOMIAL INTERPOLATION PowerPoint Presentation, free download Linear Interpolation Derivation Where a = unknown coefficients, i = 0 n. ( n + 1 coefficients). it’s form is (expressed as a power series): G(x) f(x 1) f(x) f(x 0) x. Linear interpolation is obtained by passing a straight line between 2 data points. interpolation is the problem of tting a smooth curve through a given set of points, generally. Linear Interpolation Derivation.
From www.researchgate.net
60 From up to down linear interpolation of the position of axis 2 Linear Interpolation Derivation we present linear, cubic hermite, and cubic spline interpolation methodologies, outlining the underlying assumptions and structural. X = ao + a1x + a2x2 + a3x3 + + anxn. Where a = unknown coefficients, i = 0 n. interpolation is the problem of tting a smooth curve through a given set of points, generally as the graph of a. Linear Interpolation Derivation.
From theeducationlife.com
Linear Interpolation Formula The Education Linear Interpolation Derivation it’s form is (expressed as a power series): interpolation is the problem of tting a smooth curve through a given set of points, generally as the graph of a function. Where a = unknown coefficients, i = 0 n. since it is a linear interpolation, just consider a straight line $y=a+ bx$ which goes through two points. Linear Interpolation Derivation.
From studyflix.de
Lineare Interpolation • einfach erklärt · [mit Video] Linear Interpolation Derivation Linear interpolation is obtained by passing a straight line between 2 data points. ( n + 1 coefficients). it’s form is (expressed as a power series): we present linear, cubic hermite, and cubic spline interpolation methodologies, outlining the underlying assumptions and structural. X = ao + a1x + a2x2 + a3x3 + + anxn. interpolation is the. Linear Interpolation Derivation.
From www.youtube.com
Derivation of Linear interpolation formula YouTube Linear Interpolation Derivation ( n + 1 coefficients). G(x) f(x 1) f(x) f(x 0) x. we present linear, cubic hermite, and cubic spline interpolation methodologies, outlining the underlying assumptions and structural. X = ao + a1x + a2x2 + a3x3 + + anxn. since it is a linear interpolation, just consider a straight line $y=a+ bx$ which goes through two points. Linear Interpolation Derivation.
From www.researchgate.net
59 From up to down linear interpolation of the position of axis 2 Linear Interpolation Derivation it’s form is (expressed as a power series): X = ao + a1x + a2x2 + a3x3 + + anxn. Where a = unknown coefficients, i = 0 n. ( n + 1 coefficients). since it is a linear interpolation, just consider a straight line $y=a+ bx$ which goes through two points $(x_0,y_0)$ and. Linear interpolation is obtained. Linear Interpolation Derivation.
From www.youtube.com
Linear Interpolation YouTube Linear Interpolation Derivation X = ao + a1x + a2x2 + a3x3 + + anxn. Where a = unknown coefficients, i = 0 n. we present linear, cubic hermite, and cubic spline interpolation methodologies, outlining the underlying assumptions and structural. G(x) f(x 1) f(x) f(x 0) x. interpolation is the problem of tting a smooth curve through a given set of. Linear Interpolation Derivation.
From kunduz.com
Linear Interpolation Formula Definition, Derivation, Solved Examples Linear Interpolation Derivation ( n + 1 coefficients). interpolation is the problem of tting a smooth curve through a given set of points, generally as the graph of a function. X = ao + a1x + a2x2 + a3x3 + + anxn. Linear interpolation is obtained by passing a straight line between 2 data points. it’s form is (expressed as a. Linear Interpolation Derivation.
From www.youtube.com
Linear Interpolation Explained What is a linear interpolation? YouTube Linear Interpolation Derivation we present linear, cubic hermite, and cubic spline interpolation methodologies, outlining the underlying assumptions and structural. since it is a linear interpolation, just consider a straight line $y=a+ bx$ which goes through two points $(x_0,y_0)$ and. ( n + 1 coefficients). X = ao + a1x + a2x2 + a3x3 + + anxn. Linear interpolation is obtained by. Linear Interpolation Derivation.
From www.youtube.com
ALL ABOUT Linear Interpolation Concept, Application, and Derivation Linear Interpolation Derivation X = ao + a1x + a2x2 + a3x3 + + anxn. it’s form is (expressed as a power series): since it is a linear interpolation, just consider a straight line $y=a+ bx$ which goes through two points $(x_0,y_0)$ and. Where a = unknown coefficients, i = 0 n. we present linear, cubic hermite, and cubic spline. Linear Interpolation Derivation.
From www.youtube.com
Linear InterpolationAn Easy Way YouTube Linear Interpolation Derivation X = ao + a1x + a2x2 + a3x3 + + anxn. it’s form is (expressed as a power series): we present linear, cubic hermite, and cubic spline interpolation methodologies, outlining the underlying assumptions and structural. ( n + 1 coefficients). Where a = unknown coefficients, i = 0 n. interpolation is the problem of tting a. Linear Interpolation Derivation.
From www.researchgate.net
Linear interpolation. Download Scientific Diagram Linear Interpolation Derivation it’s form is (expressed as a power series): Linear interpolation is obtained by passing a straight line between 2 data points. since it is a linear interpolation, just consider a straight line $y=a+ bx$ which goes through two points $(x_0,y_0)$ and. ( n + 1 coefficients). we present linear, cubic hermite, and cubic spline interpolation methodologies, outlining. Linear Interpolation Derivation.
From www.datadigitization.com
Linear Interpolation Equation Dagra Data Digitizer Linear Interpolation Derivation ( n + 1 coefficients). G(x) f(x 1) f(x) f(x 0) x. since it is a linear interpolation, just consider a straight line $y=a+ bx$ which goes through two points $(x_0,y_0)$ and. interpolation is the problem of tting a smooth curve through a given set of points, generally as the graph of a function. Where a = unknown. Linear Interpolation Derivation.
From www.youtube.com
Lesson 4 Linear Interpolation with Thermodynamic Tables YouTube Linear Interpolation Derivation Linear interpolation is obtained by passing a straight line between 2 data points. we present linear, cubic hermite, and cubic spline interpolation methodologies, outlining the underlying assumptions and structural. since it is a linear interpolation, just consider a straight line $y=a+ bx$ which goes through two points $(x_0,y_0)$ and. interpolation is the problem of tting a smooth. Linear Interpolation Derivation.
From studylib.net
Piecewise linear interpolation Linear Interpolation Derivation Linear interpolation is obtained by passing a straight line between 2 data points. X = ao + a1x + a2x2 + a3x3 + + anxn. it’s form is (expressed as a power series): since it is a linear interpolation, just consider a straight line $y=a+ bx$ which goes through two points $(x_0,y_0)$ and. interpolation is the problem. Linear Interpolation Derivation.
From engcourses-uofa.ca
Engineering at Alberta Courses » Quadratic Spline Interpolation Linear Interpolation Derivation it’s form is (expressed as a power series): X = ao + a1x + a2x2 + a3x3 + + anxn. G(x) f(x 1) f(x) f(x 0) x. Where a = unknown coefficients, i = 0 n. since it is a linear interpolation, just consider a straight line $y=a+ bx$ which goes through two points $(x_0,y_0)$ and. interpolation. Linear Interpolation Derivation.
From www.chegg.com
Solved TwoPoint Linear Interpolation The equation of the Linear Interpolation Derivation G(x) f(x 1) f(x) f(x 0) x. Linear interpolation is obtained by passing a straight line between 2 data points. Where a = unknown coefficients, i = 0 n. since it is a linear interpolation, just consider a straight line $y=a+ bx$ which goes through two points $(x_0,y_0)$ and. interpolation is the problem of tting a smooth curve. Linear Interpolation Derivation.